There are many possible causes of hearing loss. The most common cause – so-called age-related hearing loss (also known as presbyacusis) – is not a disease, but is due to the biological aging process. After the auditory exam, the hearing care professional can say if you have a Sensorineural hearing loss or a conductive hearing loss.
A mixed hearing loss is also possible. The causes for them can be fairly obvious in some cases as you can see in the list below but in other cases, sophisticated tests in combination with the past medical history can show the cause of the hearing loss.
Other causes may include:
Sensorineural Hearing Loss:
Sensorineural hearing loss makes up 80% of all hearing loss. The cause can be a damaged part of the inner ear which leads to
- Exposure to loud noise
- Aging (presbycusis)
- Head trauma
- Virus or disease
- Autoimmune inner ear disease
- Heredity factors (familial hearing loss)
- Malformation of the inner ear
- Ménière’s disease
- Auditory nerve damage, e.g. tumor of the auditory nerve (acoustic neuroma
When it comes to sensorineural hearing loss, the part of the auditory pathway that is responsible for processing sound events is affected. These are the inner ear with the organ of Corti, the auditory nerves, the auditory pathway components in the brainstem as well as the centrally processing structures in the brain.
Depending on what caused the sensorineural hearing loss different structures will be affected. For example, Sensorineural disorders are divided according to their localization into:
Cochlear (Localized in the Cochlea) Hearing Loss
- pancochlear (entire frequency range)
- apicocochlear (low frequency hearing loss)
- basocochlear (high frequency hearing loss)
- mediocochlear (middle frequency hearing loss)
But the hearing loss could also be caused by structures behind the cochlear in such a case hearing care professionals speak from a retrocochlear hearing loss.
Retrocochlear (Behind the Cochlea) Hearing Loss
If disturbances occur in the cochlear nerve and in structures of the auditory pathway in the brainstem, in tumors (e.g. acoustic neuroma), in disturbed neuronal development (e.g. in newborns with kernicterus, in malformations, we are speaking of:
- Central hearing loss (located in central structures of the auditory pathway)
- Auditory perception disorders (disorders of auditory processing)
Conductive Hearing Loss:
Conductive hearing loss usually offers good chances for treatment. Depending on the cause of the conductive hearing loss, the treatment must be adapted by the ENT physician. This type of hearing loss makes up 10-20% of all hearing loss.
- Otosclerosis (ossification of the joints of the auditory ossicles)
- Consequence of (repeated) inflammatory processes, especially in the middle ear – e.g. chronic middle ear inflammation in childhood, consequence of childhood diseases such as measles, mumps or scarlet fever
- Buildup of earwax
- Fluid in the ear
- Foreign body in the ear
- Eustachian tube malfunction
- Cholesteatoma (tumor of the middle ear)
In the chart below you can see where the types of hearing losses have stemmed from and how treatment would look like. When it comes to Sensorineural hearing loss a big factor is how much noise you have in your environment and how you are exposed to this noise. The simplest thing in such a case is to prevent your hearing from damage by using ear protection.
But other causes as you saw can be hereditary or side effects from medicine which can be hard to avoid.
| Conductive hearing loss | Sensorineural hearing loss | |
| What causes the disturbance? | Sound transmission disturbance | Sensory or neuronal defect |
| Where is the cause of the hearing loss located? | outer ear area or middle ear | The inner ear, auditory nerve, or auditory pathway in the brain |
| What kind of treatment is available? | Surgical and/or drug removal/remediation of the cause. | Surgery/medication only in rare cases; compensation of hearing loss with a hearing aid or cochlear implant. |
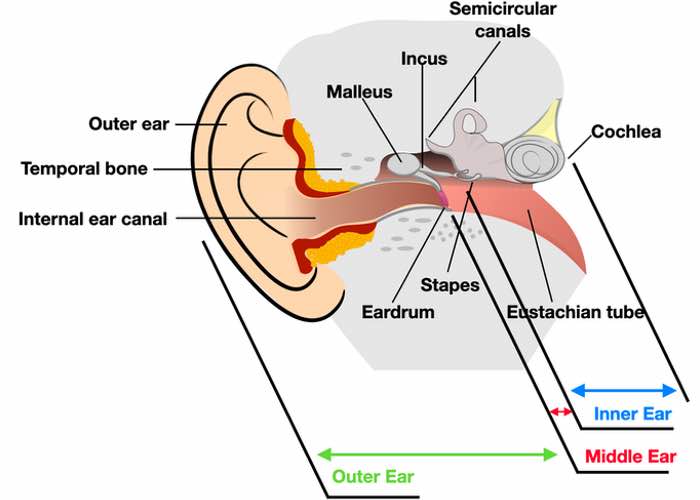
Here in the image above you can see where the areas are which cause one of the mentioned types of hearing loss. Combinations of them are also always possible. Down below you can read more about mixed hearing loss.
Mixed Hearing Loss
When both forms of hearing loss are present, they must be treated separately. First, you will be diagnosed with combined hearing loss using an audiogram. This allows your audiologist to determine what is causing your conductive hearing loss.
The part of the mixed hearing loss which is caused by tumors or earwax buildup may be removed with procedures to get rid of these blockages. Infections of the outer ear can cause conductive hearing loss as well. This may be treated with antibiotics. When those blockages are gone after the procedures to remove them the hearing care professional can then focus on the sensorineural hearing loss.
This type of hearing loss can not be removed because here we have damaged hair cells for example. Those cells transmit an electrical code when a soundwave enters our ears which describes the auditory world to the brain. When they are not working correctly a hearing aid with more amplification is able to stimulate them again.
Sensorineural hearing loss can be more difficult to treat. Because the way how the person hears is different with hearing aids compared to natural hearing. If you want to find out more on this topic I wrote you an article here. Although modern hearing aids get better with every release cycle they can not give you the hearing back you experienced before the hearing loss. But sure a lot of patients with hearing loss will not miss them either.
A complete hearing check will show what type of hearing loss may hinder you from hearing optimally. This requires the hearing care professional to use headphones that predominantly stimulate your ear over the air but also with bone conductive receivers which stimulate your ear with vibration.
In the video above you will find additional information on how your audiogram may look like depending on what caused your hearing loss. He goes through the different types of hearing losses mentioned in the paragraphs above and what changes with a sensorineural or conductive or mixed hearing loss.
